Malayalam Content from Real estate Reels
ആദ്യമായ് നമ്മൾ പഠിക്കുന്നത് ചില പുതിയ വാക്കുകളും അവയുടെ ശരിയായ അർത്ഥങ്ങളും ആണ്. നമ്മൾ മലയാളത്തിൽ വിചാരിച്ചു വച്ചിരിക്കുന്ന അർഥം ചിലപ്പോൾ മാത്രമേ ശരിയാവുകയുള്ളു. സാഹചര്യം അനുസരിച്ചും അർഥം മാറാം. ഒരു നൂറു വാക്കുകളുടെ അർത്ഥം ശരിയായി മനസിലാക്കിയാൽ നമ്മൾ പകുതി കാര്യവും പഠിച്ചിരിക്കും.
കാര്യങ്ങൾ ഇംഗ്ലീഷിലും മലയാളത്തിലും മാറി മാറി കൊടുത്തിരിക്കുന്നു. റിയൽ എസ്റ്റേറ്റ് പരീക്ഷക്കു തയാറാവുന്നവർക്കു ഇത് തികച്ചും ഉപകാരപ്രദമാകും .
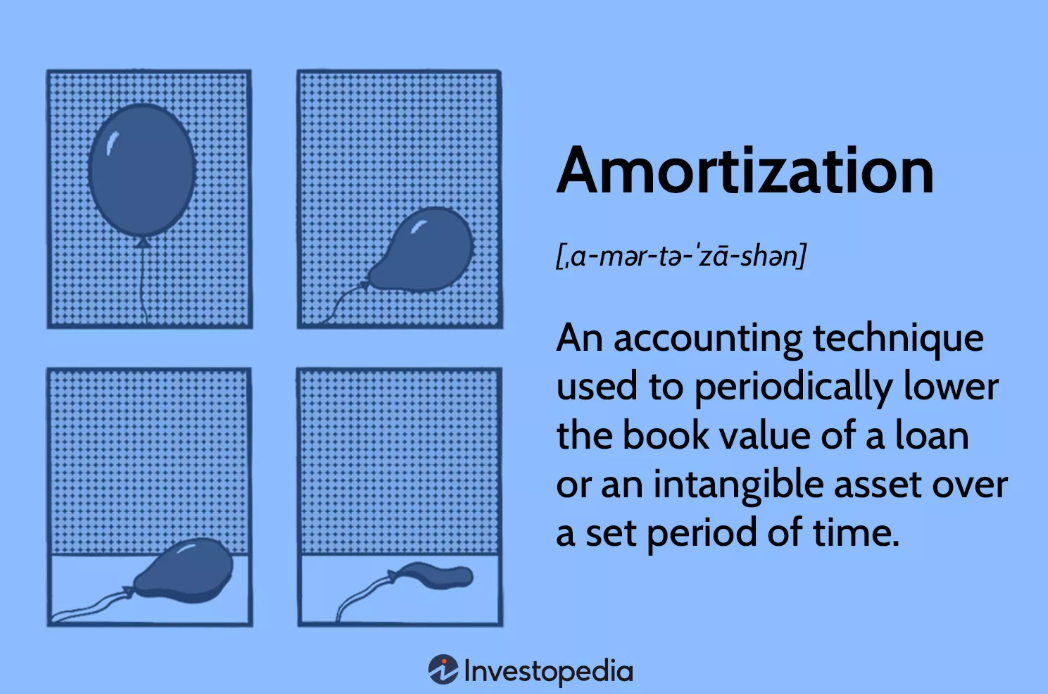
Amortization
Amortization is the process of paying off a debt over a time period in equal installments. Amortization is an accounting technique used to periodically reduce the book value of a loan or an intangible asset over a specified period. Concerning a loan, amortization focuses on spreading out loan payments over time. When applied to an asset, amortization is similar to depreciation.
അമോർട്ടൈസേഷൻ എന്നത് തുല്യമായ തവണ(EMI)കളിലൂടെ ഒരു നിശ്ചിത കാലയളവിൽ (Term) കടം തിരിച്ചു അടയ്ക്കുന്ന പ്രക്രിയ ആണ് .അമോർട്ടൈസേഷൻ എന്നത് ധനകാര്യ, അക്കൗണ്ടിംഗ് മേഖലകളിലെ ഒരു പ്രധാന സങ്കല്പമാണ്, ഇത് കടങ്ങളുടെയും (ചില തരം )അദൃശ്യ ആസ്തികളുടെയും മൂല്യം ( book Value) ഒരു നിശ്ചിത കാലയളവിൽ ക്രമാനുഗതമായി കുറയുന്നതിനെ ആണ് കാണിക്കുന്നത് .ഒരു വായ്പയുടെ കാര്യത്തിൽ, അമോർട്ടൈസേഷൻ എന്നത് വായ്പയുടെ മുതലും പലിശയും ഒരു നിശ്ചിത കാലയളവിൽ, ഉദാഹരണത്തിന്, പ്രതിമാസമോ വാർഷികമോ ആയ തവണകളായി തിരിച്ചു അടയ്ക്കുന്ന പ്രക്രിയയാണ്. ഒരു ആസ്തിയുടെ കാര്യം എടുത്താൽ അമോർട്ടൈസേഷൻ എന്നത് ഡിപ്രീസിയേഷന് സമാനമാണ് .
Amortization is a fundamental financial and accounting concept that plays a critical role in managing debts and assets over time. At its core, amortization refers to the systematic process of paying off a debt or reducing the value of an asset in a structured manner, typically through equal periodic payments over a specified period. This process ensures that the financial obligation or asset value is gradually reduced in a predictable and manageable way.
അമോർട്ടൈസേഷൻ എന്നത് ഒരുനിശ്ചിത കാലയളവിൽ കടം തിരിച്ചടയ്ക്കുന്നതിനോ അല്ലെങ്കിൽ ഒരു ആസ്തിയുടെ (asset) മൂല്യം കുറച്ചു കണക്കാക്കുന്നതിനോ (A term similar to depreciation) ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്ന ഒരു അടിസ്ഥാനപരമായ സാമ്പത്തിക അക്കൗണ്ടിംഗ് രീതി ആണ്. ഇത് സാധാരണയായി ഒരു സാമ്പത്തിക ബാധ്യതയോ (loan) ആസ്തി മൂല്യമോ (Asset value - depreciation) ക്രമാനുഗതമായി, ഒരു നിശ്ചിത കാലയളവിൽ കുറയ്ക്കുന്നതിന് ഉള്ള രീതിയാണ്.ഈ പ്രക്രിയ സാമ്പത്തിക ബാധ്യതയെ അഥവാ ആസ്തി മൂല്യത്തെ ക്രമമായി കുറയ്ക്കുന്നതിന് ഉള്ള, മുൻകൂട്ടി കണ്ടു manage ചെയ്യാവുന്ന രീതിയാണ് .
When applied to a loan, amortization involves spreading out the repayment of the principal amount and interest over a fixed period, such as monthly or yearly installments. Each payment covers a portion of the principal (the original loan amount) and the interest accrued on the remaining balance. Over time, as the principal decreases, the interest portion of each payment reduces, while the portion applied to the principal increases. This structured repayment schedule allows borrowers to plan their finances effectively and ensures that the loan is fully paid off by the end of the term. For example, a home mortgage or a car loan often follows an amortization schedule, where the borrower makes regular payments that systematically reduce the debt over years.
ഒരു കടബാധ്യതയെ സംബന്ധിച്ചിടത്തോളം അമോർട്ടൈസേഷൻ എന്നത് മുതലിന്റെ ഒരു ഭാഗവും വായ്പയുടെ യഥാർത്ഥ തുക) ബാക്കി നിൽക്കുന്ന തുകയുടെ അന്നത്തെ ദിവസം വരെയുള്ള പലിശയും സമമായ തവണകളായി (EMI- Equal Monthly Instalment) കണക്കാക്കുന്നത് ആണ് . ഓരോ തവണയും തിരിച്ചു അടയ്ക്കുമ്പോൾ മുതലിന്റെ ഒരു ഭാഗവും ബാക്കി നിൽക്കുന്ന തുകയിൽമേൽ ഉള്ള പലിശയും കുറഞ്ഞു കൊണ്ടിരിക്കും. കാലക്രമേണ, മുതൽ കുറയുമ്പോൾ, ഓരോ തിരിച്ചടവ് തവണയിലേയും പലിശയുടെ ഭാഗം കുറയുകയും മുതലിന് ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്ന ഭാഗം വർദ്ധിക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു. ഈ ഘടനാപരമായ തിരിച്ചടവ് (ഷെഡ്യൂൾ) shecduled repayment വായ്പക്കാർക്ക് അവരുടെ സാമ്പത്തികം ഫലപ്രദമായി ആസൂത്രണം ചെയ്യാൻ അനുവദിക്കുകയും, വായ്പാ കാലാവധി അവസാനിക്കുമ്പോൾ കടം പൂർണ്ണമായി തിരിച്ചടയ്ക്കപ്പെടുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു. ഉദാഹരണത്തിന്, ഒരു ഭവന വായ്പ (മോർട്ട്ഗേജ്) അല്ലെങ്കിൽ കാർ വായ്പ (loan) പലപ്പോഴും ഒരു അമോർട്ടൈസേഷൻ ഷെഡ്യൂൾ പിന്തുടരുന്നു, അവിടെ വായ്പക്കാർ വർഷങ്ങൾ കൊണ്ട് കടം ക്രമാനുഗതമായി കുറയ്ക്കുന്നു.
In the context of accounting, amortization also applies to intangible assets, such as patents, trademarks, or goodwill. Unlike tangible assets like machinery, which lose value through depreciation, intangible assets are amortized. Amortization in this sense involves gradually reducing the book value of the intangible asset over its useful life. This process reflects the consumption or expiration of the asset’s economic benefits. For instance, if a company purchases a patent with a 10-year lifespan, the cost of the patent is spread out evenly over those 10 years through amortization, reducing its recorded value on the balance sheet each year.
അക്കൗണ്ടിംഗിന്റെ (In accounting) സന്ദർഭത്തിൽ, അമോർട്ടൈസേഷൻ അദൃശ്യമായ ആസ്തികൾക്കും (intangible assets) ബാധകമാണ്, ഉദാഹരണത്തിന്, പേറ്റന്റുകൾ, ട്രേഡ്മാർക്കുകൾ, അല്ലെങ്കിൽ ഗുഡ്വിൽ. യന്ത്രങ്ങൾ (Vehicles/ furniture/ building etc.) പോലുള്ള ദൃശ്യമായ ആസ്തികളുടെ (tangible assets) മൂല്യം കുറയ്ക്കുന്നതിന് ഡിപ്രീസിയേഷൻ (എന്ന പദം ) ഉപയോഗിക്കുമ്പോൾ, ദൃശ്യമായ ആസ്തികൾ(ക്ക് ) അമോർട്ടൈസേഷൻ വഴി മൂല്യം കുറയ്ക്കുന്നു. ഈ അർത്ഥത്തിൽ,അമോർട്ടൈസേഷൻ എന്നത് ആസ്തിയുടെ ഉപയോഗപ്രദമായ ആയുസ്സിന്റെ (useful life) കാലയളവിൽ അതിന്റെ ബുക്ക് മൂല്യം Book Value ക്രമാനുഗതമായി കുറയ്ക്കുന്ന പ്രക്രിയയാണ്. ഇത് ആസ്തിയുടെ സാമ്പത്തിക നേട്ടങ്ങളുടെ ഉപഭോഗത്തെ അല്ലെങ്കിൽ കാലഹരണപ്പെടലിനെ പ്രതിഫലിപ്പിക്കുന്നു. ഉദാഹരണത്തിന്, ഒരു കമ്പനി 10 വർഷത്തെ ആയുസ്സുള്ള ഒരു പേറ്റന്റ് വാങ്ങുകയാണെങ്കിൽ, ആ പേറ്റന്റിന്റെ മൂല്യം 10 വർഷത്തേക്ക് തുല്യമായി വിതരണം ചെയ്യപ്പെടുകയും, ഓരോ വർഷവും ബാലൻസ് ഷീറ്റിൽ അതിന്റെ രേഖപ്പെടുത്തിയ മൂല്യം കുറയ്ക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു.
In both cases—loan repayment and intangible asset valuation—amortization serves to allocate costs systematically over time, providing clarity and consistency in financial reporting and planning. It helps businesses and individuals manage long-term financial commitments and ensures compliance with accounting standards. By spreading costs or payments evenly, amortization promotes financial stability and transparency.
വായ്പ തിരിച്ചടവിന്റെയും അദൃശ്യ ആസ്തി മൂല്യ നിർണ്ണയത്തിന്റെയും കാര്യത്തിൽ, അമോർട്ടൈസേഷൻ, പേയ്മെന്റുകൾ ഒരു കാലയളവിലേക്ക് തുല്യമായി നിശ്ചയിച്ചു വയ്ക്കാൻ സഹായിക്കുന്നു(ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു). ഇത് സാമ്പത്തിക റിപ്പോർട്ടിംഗിനും ആസൂത്രണത്തിനും വ്യക്തതയും സ്ഥിരതയും നൽകുന്നു. ഇത് ബിസിനസുകൾക്കും വ്യക്തികൾക്കും ദീർഘകാല സാമ്പത്തിക ബാധ്യതകൾ കൈകാര്യം ചെയ്യാൻ സഹായിക്കുകയും, അക്കൗണ്ടിംഗ് മാനദണ്ഡങ്ങൾ പാലിക്കുന്നുവെന്ന് ഉറപ്പാക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു. ചെലവുകളോ പേയ്മെന്റുകളോ തുല്യമായി വീതിക്കപ്പെടുന്നതിലൂടെ, അമോർട്ടൈസേഷൻ സാമ്പത്തിക സ്ഥിരതയും സുതാര്യതയും പ്രോത്സാഹിപ്പിക്കുന്നു.
അമോർട്ടൈസേഷൻ എന്താണ്?
അമോർട്ടൈസേഷൻ എന്നത് ഒരു കടം അല്ലെങ്കിൽ ആസ്തിയുടെ മൂല്യം കുറച്ചു കണക്കാക്കുന്നതിനുള്ള ഒരു എളുപ്പമുള്ള രീതിയാണ്. ഇത് ഒരു നിശ്ചിത കാലയളവിൽ തുല്യമായ തുകകൾ (തവണകൾ) ആയി വിഭജിച്ച് ചെയ്യുന്നു.
വായ്പയുടെ കാര്യത്തിൽ:
നമ്മൾ ഒരു വായ്പ എടുക്കുമ്പോൾ, അത് തിരിച്ചടയ്ക്കാൻ അമോർട്ടൈസേഷൻ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു. വായ്പയുടെ മുഴുവൻ തുകയും പലിശയും തുല്യമായ പ്രതിമാസ അല്ലെങ്കിൽ വാർഷിക തവണകളായി വിഭജിക്കുന്നു. ഓരോ തവണയും, ഒരു ഭാഗം വായ്പയുടെ മുതലിനും (യഥാർത്ഥ തുക) മറ്റൊരു ഭാഗം പലിശയ്ക്കും പോകുന്നു. കാലക്രമേണ, മുതൽ കുറയുമ്പോൾ, തിരിച്ചടവിൽ പലിശ ഭാഗം കുറയുകയും മുതലിന്റെ ഭാഗം കൂടുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു. ഉദാഹരണത്തിന്, ഒരു വീടിനോ കാറിനോ വേണ്ടി എടുത്ത വായ്പ ഇങ്ങനെ തിരിച്ചടയ്ക്കാം. അവസാനം, വായ്പ പൂർണ്ണമായി തീർക്കപ്പെടും.
ആസ്തിയുടെ കാര്യത്തിൽ:
അമോർട്ടൈസേഷൻ അദൃശ്യ ആസ്തികൾക്കും (intangible assets) ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു, ഉദാഹരണത്തിന്, പേറ്റന്റുകൾ അല്ലെങ്കിൽ ട്രേഡ്മാർക്കുകൾ. ഈ ആസ്തികളുടെ മൂല്യം അവയുടെ ഉപയോഗ കാലത്തിനനുസരിച്ച് ഓരോ വർഷവും കുറയ്ക്കുന്നു. ഉദാഹരണത്തിന്, 10 വർഷം ഉപയോഗിക്കാവുന്ന ഒരു പേറ്റന്റിന്റെ മൂല്യം 10 വർഷത്തേക്ക് തുല്യമായി വിഭജിച്ച് കുറയ്ക്കുന്നു. ഇത് കമ്പനിയുടെ ബാലൻസ് ഷീറ്റിൽ കൃത്യമായി രേഖപ്പെടുത്താൻ സഹായിക്കുന്നു.
എന്തുകൊണ്ട് ഇത് പ്രധാനമാണ്?
അമോർട്ടൈസേഷൻ കടങ്ങളും ആസ്തികളും എളുപ്പമായി കൈകാര്യം ചെയ്യാൻ സഹായിക്കുന്നു. ഇത് സാമ്പത്തിക ആസൂത്രണം വ്യക്തമാക്കുകയും കടം തിരിച്ചടയ്ക്കലോ ആസ്തി മൂല്യം കുറയ്ക്കലോ ക്രമമായി നടക്കുന്നുവെന്ന് ഉറപ്പാക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു.
.
English Explanation: Mortgage Amortization Example
Let’s calculate the monthly payment for a $300,000 mortgage with a 30-year term and a 5% annual interest rate, assuming a fixed-rate loan. We’ll then show how the amortization process works by breaking down the payments into principal and interest over time.
Step 1: Calculate the Monthly Payment. No need to remember this formula
Using a financial calculator or formula:
So, the monthly payment is approximately $1,610.46.
Step 2: Amortization Breakdown
We split each monthly payment of $1,610.46 into two categories:
- Interest: Based on the remaining principal balance.
- Principal: The portion that reduces the loan balance.
Here’s how it works for the first few payments and over time:
- Month 1:
- Interest = Remaining balance × Monthly rate = $300,000 × (5 percent per year/12 months) = $300000X004167= $1,250.10
- Principal = Total payment - Interest = $1,610.46 - $1,250.10 = $360.36
- New balance = $300,000 - $360.36 = $299,639.64
- Month 2:
- Interest = $299,639.64 × 0.004167 = $1,248.60
- Principal = $1,610.46 - $1,248.60 = $361.86
- New balance = $299,639.64 - $361.86 = $299,277.78
Over time, as the principal decreases, the interest portion shrinks, and the principal portion grows. By the end of 30 years (360 payments), the loan balance reaches $0.
Sample Amortization Table
Below is a simplified table showing the first three months and the final month:
|
Month |
Payment |
Interest |
Principal |
Balance |
|
1 |
$1,610.46 |
$1,250.10 |
$360.36 |
$299,639.64 |
|
2 |
$1,610.46 |
$1,248.60 |
$361.86 |
$299,277.78 |
|
3 |
$1,610.46 |
$1,247.10 |
$363.36 |
$298,914.42 |
|
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
|
360 |
$1,610.46 |
$6.71 |
$1,603.75 |
$0.00 |
Key Points for the Lecture
- The total amount paid over 30 years = $1,610.46 × 360 = $579,765.60, of which $300,000 is principal, and $279,765.60 is interest.
- Early payments mostly cover interest, while later payments mostly reduce the principal.
- This predictable schedule helps borrowers plan their finances.
Simplified Malayalam Translation for the Academic Lecturing Video
വീടിന്റെ വായ്പ: ഒരു ഉദാഹരണം (അമോർട്ടൈസേഷൻ)
നമുക്ക് ഒരു $300,000 (3 ലക്ഷം ഡോളർ) വായ്പ എടുക്കുന്നതിനെക്കുറിച്ച് നോക്കാം. ഇത് 30 വർഷത്തേക്കുള്ള വായ്പയാണ്, 5% വാർഷിക പലിശ (interest) ഉള്ളത്. ഈ വായ്പ തിരിച്ചടയ്ക്കാൻ അമോർട്ടൈസേഷൻ എങ്ങനെ പ്രവർത്തിക്കുന്നുവെന്ന് നോക്കാം.
പ്രതിമാസ തിരിച്ചടവ്
ഈ വായ്പയുടെ പ്രതിമാസ തിരിച്ചടവ് കണക്കാക്കാൻ ഒരു ഫോർമുല ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു.
- വായ്പ തുക = $300,000
- വാർഷിക പലിശ = 5%, അതായത് പ്രതിമാസ പലിശ = 0.05 ÷ 12 = 0.004167
- തവണകളുടെ എണ്ണം = 30 വർഷം × 12 മാസം = 360
കണക്കുകൂട്ടിയാൽ, പ്രതിമാസം $1,610.46 (ഏകദേശം 1.35 ലക്ഷം രൂപ) തിരിച്ചടയ്ക്കണം.
തവണകൾ എങ്ങനെ വിഭജിക്കപ്പെടുന്നു?
ഓരോ $1,610.46 തവണയും രണ്ട് ഭാഗങ്ങളായി വിഭജിക്കപ്പെടുന്നു:
- പലിശ: ബാക്കി വായ്പ തുകയെ അടിസ്ഥാനമാക്കി.
- മുതൽ: വായ്പയുടെ യഥാർത്ഥ തുക കുറയ്ക്കുന്ന ഭാഗം.
ഉദാഹരണം:
- ആദ്യ മാസം:
- പലിശ = $300,000 × 0.004167 = $1,250.10
- മുതൽ = $1,610.46 - $1,250.10 = $360.36
- പുതിയ ബാലൻസ് = $300,000 - $360.36 = $299,639.64
- രണ്ടാം മാസം:
- പലിശ = $299,639.64 × 0.004167 = $1,248.60
- മുതൽ = $1,610.46 - $1,248.60 = $361.86
- പുതിയ ബാലൻസ് = $299,639.64 - $361.86 = $299,277.78
കാലക്രമേണ, മുതൽ കുറയുമ്പോൾ പലിശ കുറയുകയും, മുതലിന്റെ ഭാഗം കൂടുകയും ചെയ്യും. 360 മാസങ്ങൾക്ക് ശേഷം (30 വർഷം), വായ്പ പൂർണ്ണമായി തീർക്കപ്പെടും.
ഒരു ലളിതമായ ടേബിൾ
|
മാസം |
തവണ |
പലിശ |
മുതൽ |
ബാക്കി തുക |
|
1 |
$1,610.46 |
$1,250.10 |
$360.36 |
$299,639.64 |
|
2 |
$1,610.46 |
$1,248.60 |
$361.86 |
$299,277.78 |
|
3 |
$1,610.46 |
$1,247.10 |
$363.36 |
$298,914.42 |
|
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
|
360 |
$1,610.46 |
$6.71 |
$1,603.75 |
$0.00 |
പ്രധാന കാര്യങ്ങൾ
- 30 വർഷം കൊണ്ട് മൊത്തം തിരിച്ചടയ്ക്കുന്ന തുക = $1,610.46 × 360 = $579,765.60. ഇതിൽ $300,000 മുതലും, $279,765.60 പലിശയുമാണ്.
- ആദ്യം, തവണയിൽ ഭൂരിഭാഗവും പലിശയാണ്. പിന്നീട്, മുതലിന്റെ ഭാഗം കൂടുതലാകും.
- ഈ ഷെഡ്യൂൾ വായ്പക്കാർക്ക് സാമ്പത്തിക ആസൂത്രണം എളുപ്പമാക്കുന്നു.
LOGIN TO REPOST THIS NEWS




LEAVE A COMMENT
Cease from posting remarks that are foul, abusive or provocative, and don't enjoy individual assaults, verbally abusing or affecting scorn against any community.Help us erase remarks don't pursue these rules by checking them hostile. We should cooperate to keep the discussion common.
COMMENTS